When you open a bar of chocolate, and look at the shiny velvety bar that melts in your hand, you should know the terms and components that go into making these delectable chocolates.
We have simplified the terminology of Chocolates, so that you will be able to understand the process and efforts put into each bar.
List of Chocolate Glossary probably you should be knowing
Artisan Chocolates:
These are chocolates made by a small group of craftsmen with in-depth knowledge of chocolates; they understand the quintessential aspects of chocolate making. Every chocolate making company that claims to produce artisanal chocolates, must have an artisan.

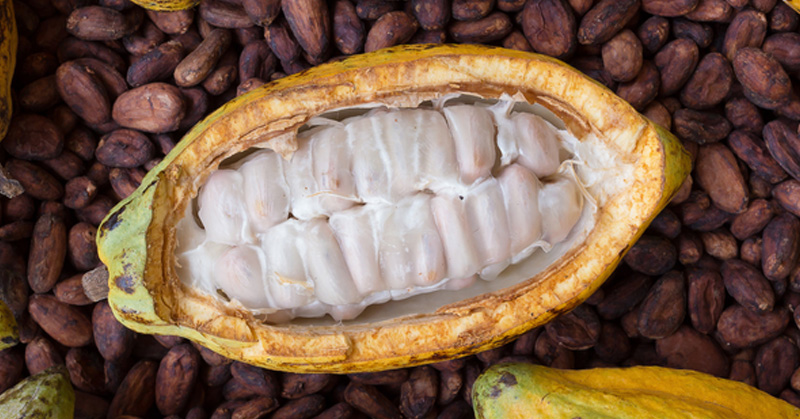
Cacao:
Cacao refers to the Theobroma cacao tree. The fruit and seeds are used in the production of cocoa. The fermented seeds of the tree are dried and used in chocolates. These seeds are called cocoa beans.
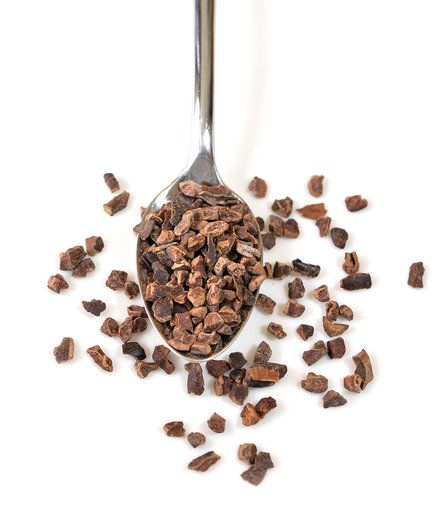
Cacao nibs:
Cacao nibs are small pieces of the cacao beans, they are crushed beans and are packed with antioxidants, nutrients, and fiber. They are bitter and have a rich chocolate flavor.

Chocolate liquor:
Chocolate liquor is just ground up cocoa nibs. It is usually in molten form, but can also be in liquid form. There is no alcohol in this and should not be mistaken for the chocolate liqueur.
Chocolate percentage or Cocoa percentage:
This percentage refers to the amount of chocolate liquor, cocoa butter, and cocoa powder present in the chocolates.
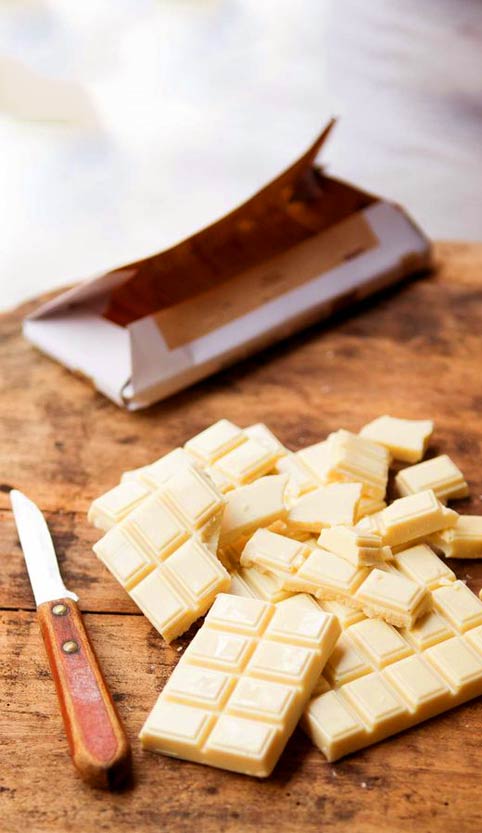
White Chocolates:
It refers to the type of chocolates without chocolate liquor. It contains only cocoa butter, sugar, and milk solids. Some chocolatiers don’t consider this as chocolate.
Chocolatiers:
A chocolatier is a person, who uses chocolate to make chocolate delicacies with unique chocolate flavors.
Terrior:
Terrior refers to the various ways a particular region, that impacts the production of cocoa, For example, the climate and soil quality.
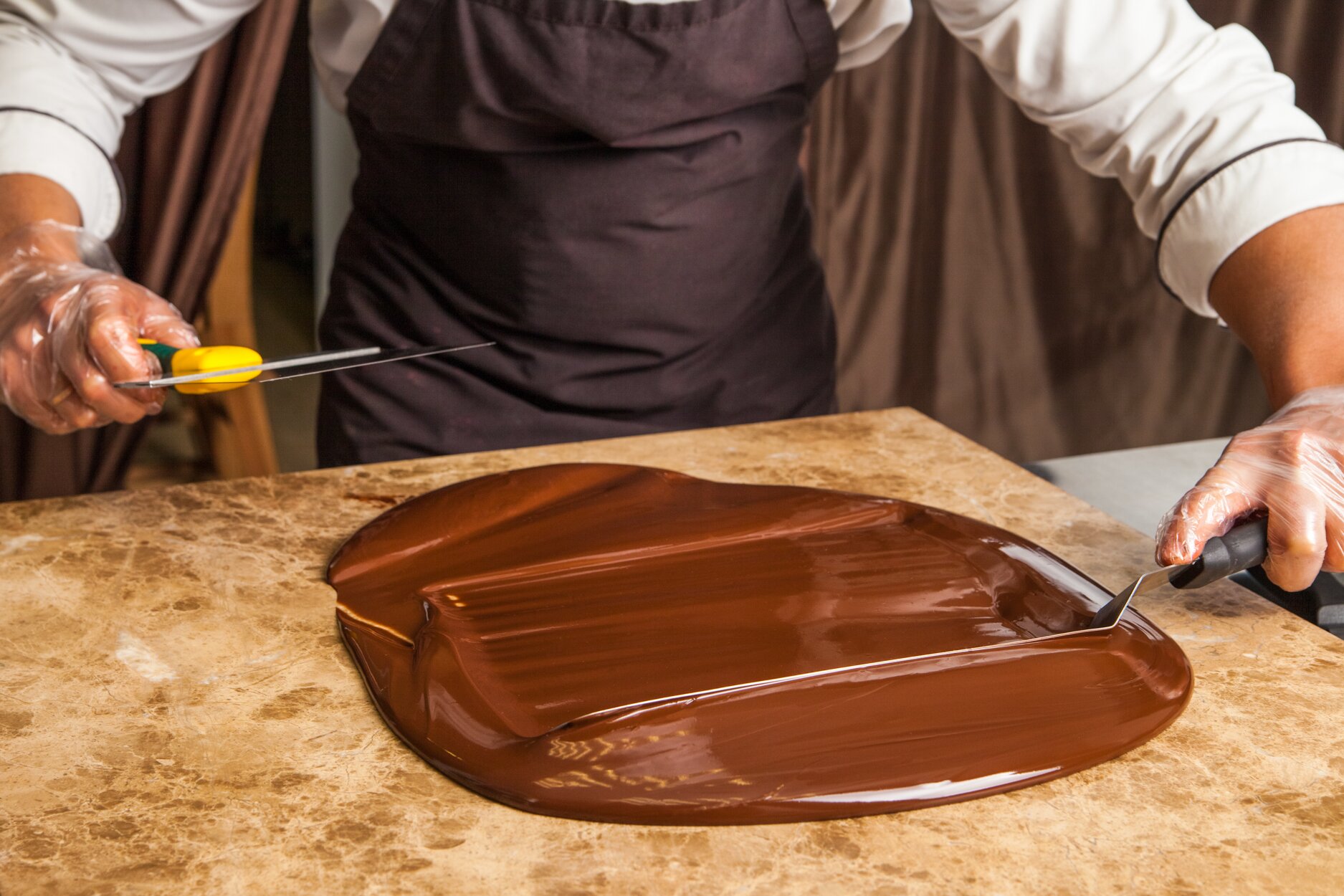
Tempering:
Chocolate Tempering refers to a process, where the cocoa butter in the chocolates is crystallized under controllable measures. Typically, the chocolate is heated and immediately cooled. This process gives chocolates its glossy sheen, and that signature snap when you bite into it.
Roasting:
This process refers to the roasting of cacao beans.This gives the beans its rich aroma and taste. The time is taken to roast the cocoa bean can be altered to give a particular taste to the chocolates. It is said that chocolates are roasted longer, and at a lower temperature than compared to coffee.

Pistoles:
Pistoles actually refers to the circular shape of the chocolates. Originally it is a French word which means gold coin, but in the world of chocolates, it represents the rounded shape of the gold coin, in which the chocolates can be molded in.
Milk Chocolates:
Milk Chocolates are the type of chocolates that has cacao liquor, cocoa butter, sugar as well as milk solids ( milk fat ).
Dark Chocolates:
Dark Chocolates are the type of chocolates, that has mostly chocolate liquor. It can contain sugar, cocoa butter, lecithin, and vanilla, but it does not contain any milk solids.

Conching:
Conching is a process to improve the flavor and texture of the chocolates, this process uses different machines called conches or refiner conches. It takes place for several hours.
Lecithin:
Lecithin is an emulsifier that decreases the viscosity of chocolates. It makes the chocolates more silky, and smooth. It is generally added at the end of the conching process. It thins out the chocolates and helps maintain the emulsion between the cocoa butter, and the sugar. Without emulsifiers, the chocolates will be dense and thick with air trapped inside.
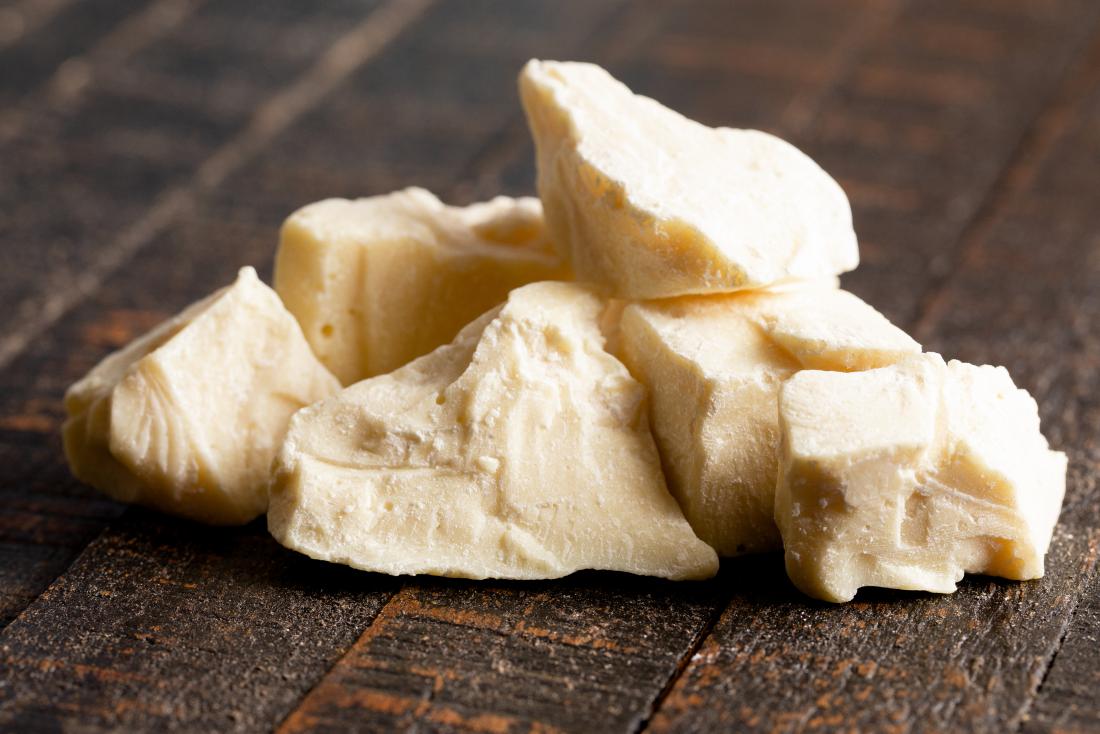
Cocoa Butter:
It is the oil extracted from the cocoa seeds (cocoa liquor). It is yellow in color and it has a wide range of uses from chocolates to pharmaceuticals .
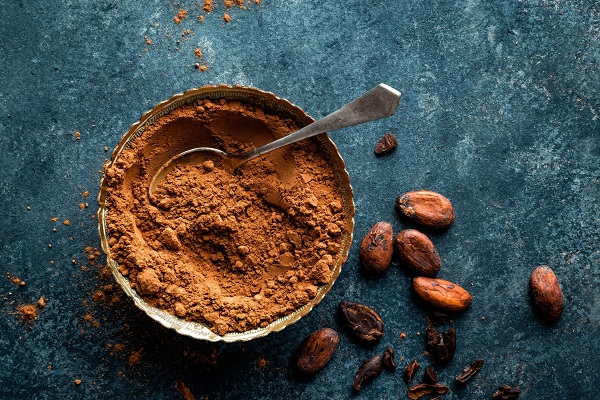
Cocoa Powder:
When the cocoa liquor is subjected to the hydraulic press, the cocoa butter is separated. And what is left behind is called the cocoa cake. This cocoa cake is grounded and sifted to form cocoa powder.
Couverture:
Couverture is the process of making chocolates with extra cocoa butter. This gives the chocolates high sheen and it is typically used for covering cakes and sweets.
Coating Chocolates:
Coating chocolates are inexpensive chocolates made by using cocoa powder ,and less expensive vegetable fat instead of cocoa butter.
Allergens:
Some chocolates contain traces of peanuts, soy, gluten, and milk products, even if the chocolates do not have this flavor. This is because the machinery used for making chocolates may have processed peanuts, soy, and milk products so there may be a trace of it. This is usually printed on chocolates to alert anyone with nut allergies or lactose intolerance.
Baking Chocolate:
These are chocolate blocks, sold exclusively for baking and incorporating. Chocolate in other recipes (such as pies, cookies, etc.), come in a wide variety of options such as milk, bittersweet, semi-sweet, and white chocolates.
Bitter/unsweetened Chocolates:
This chocolate bar contains only chocolate liquor and cocoa butter with no sugar.
Buttercream:
It is a mixture of butter and sugar, chocolate can be added in it to make “chocolate buttercream”. It is typically used to ice a cake and for frosting.
Caramel:
It is a gooey topping, often found in chocolates. It is made by heating sugar, cream, butter, and vanilla in a pot, and it is made to simmer for 15 minutes.

Dutch cocoa:
Cocoa powder, which has reduced its acidity and is more alkaline is known as dutch cocoa. It is rich in color and has more chocolate flavor. It is easier to mix with liquids.
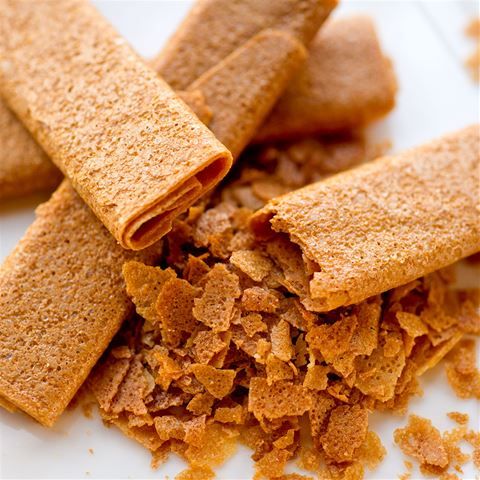
Feuilletine:
It is a delicate, thin crispy wafer. It is usually made up of pancake batter (flour, sugar, and eggs) crushed and used as a topping.
Ganache:
It is a mixture of chocolate, butter, and cream usually used to frost cake, and used in truffles.

Gianduja:
A signature combination of hazelnut paste and chocolate.
Gluten:
It is a sticky protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. Gluten is an important ingredient in bread, and it is responsible to give bread its shape.
Kosher:
This is a dietary framework according to Jewish laws and customs. They are basically Jewish laws for food preparation and processing.
Pralines:
Pralines is a crispy confection and it is made by boiling sugar and adding any nut (such as almonds, hazelnut). Traditionally bakers and chocolatiers use Hazelnut (Gianduja). You might link to check about Pecan Pralines.

Semi-Sweet chocolates:
They are chocolates containing different amounts of sugar.
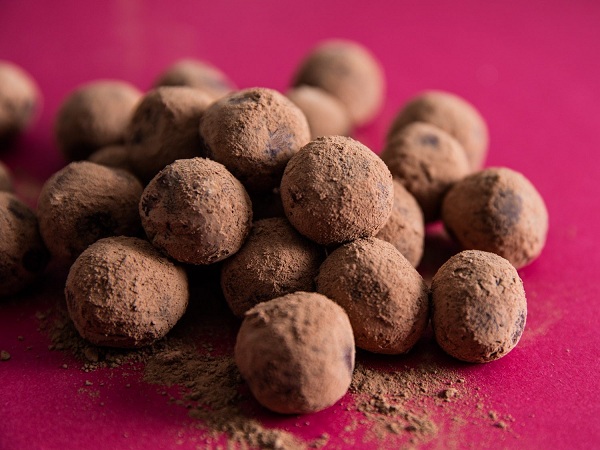
Truffles:
It is a rich, creamy and velvety confection, usually consists of rich chocolate ganache dusted with cocoa powder.
Vegan:
It is a diet that prohibits the use of animal products, such as meat and dairy products like milk and butter. Chocolates generally are not actually vegan, but since the demand for vegan food is increasing, vegan chocolates are in demand. Vegan chocolates generally use almond milk or coconut milk instead of cow/buffalo milk. As more people are switching diets, they are trying to curb animal cruelty and climate change.
Winnowing:
Winnowing is the process of removing the husk of the cocoa bean, then the cocoa nib is passed through pipes and which are then collected and sent for grinding.

Abaisse:
The French word for rolling out gianduja or nut paste. It is usually used in chocolate making.
Aftertaste:
It is the residual taste, after biting into chocolate the flavor keeps lingering on the palate.
Double Boiler:
It is a process to melt a chocolate bar. Direct flame over chocolates can burn the delicate treat to prevent these chocolates is typically melted with steam from water. The chocolates must be placed in a bowl over boiling water, although this is a traditional way to melt the chocolates. A microwave can be used.
Bean to Bar:
This term bean to bar is often printed on chocolates, and it means that the chocolates are made from scratch. Starting with the selection of beans to the roasting and grinding, and turning it into Couverture. After which they are finally made into chocolates. All of it is done by the same company.
Caffeine Content:
Chocolates do contain caffeine, but only to a small amount. Milk chocolates contain 5 mg of caffeine, and bittersweet chocolates contains 5-10 mg of caffeine .
Now that you know all the benefits and history of chocolates, rush to the nearest chocolate shop or google “best chocolate store near me” because chocolates are totally worth it.
We recommend trying out www.chocovira.in they have a wide variety of flavors, such as the classic vanilla and the dried fruits topping and also the more adventurous flavors such as the strawberry passion.